ANALISIS SENTIMENT MASYARAKAT TERHADAP PABRIK DI JAWA BARAT SEBAGAI DASAR STRATEGI PENINGKATAN CITRA INDUSTRI DI MAJALENGKA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31949/j-ensitec.v11i02.14526Abstract
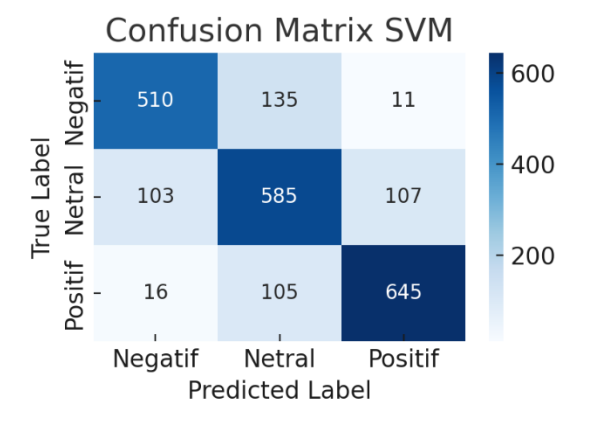
The rapid development of the new industrial estate in Majalengka requires the support of a good image from the local community. This study aims to assess public sentiment towards factories in West Java as a basis for formulating strategies to improve the image of industry in Majalengka. The Support Vector Machine (SVM) method was applied to classify the sentiment of YouTube comments relating to the factory, after a process of data collection, text preprocessing, and lexicon-based sentiment labelling. The main findings indicated that people's sentiments were distributed in proportions of approximately 30% negative, 35% neutral, and 35% positive. The accuracy of the SVM model was recorded at 78.48%, while the confusion matrix indicated adequate classification performance of the sentiments. matrix indicates adequate classification performance for negative, neutral, and positive sentiments. negative, neutral, and positive sentiments. This finding indicates that there is a significant negative sentiment towards the significant negative sentiment towards the industry, although it is not dominant. In conclusion, sentiment analysis conducted through social media can serve as a basis for formulating public relations and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) strategies. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) strategies in an effort to improve the industry's image. The industry and the government are advised to improve clear communication and responsive CSR programmes, with the aim of reducing negative sentiment and strengthening public trust. strengthen public trust.
Keywords:
Sentiment Analysis, Social Media, Support Vector Machine, Industry Image, MajalengkaDownloads
References
[1] Andriyani, D., Faqih, A. and Permana, S.E. (2025) Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Engineering Applications The Effect of SMOTE Application on Support Vector Machine Performance in Sentiment Classification on Imbalanced Datasets. Available at: https://ioinformatic.org/.
[2] Aqsha, M.R., Trianasari, N. and Sagita, A. (2025) Analisis Sentimen Dan Jaringan Sosial Tentang Polusi Udara Jakarta Di Platform Media Sosial X Sentiment And Social Network Analysis Of Jakarta Air Pollution On Social Media Platform X.
[3] Asri, Y. et al. (2025) ‘Sentiment analysis based on Indonesian language lexicon and IndoBERT on user reviews PLN mobile application’, Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 38(1), p. 677. Available at: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v38.i1.pp677-688.
[4] Baita, A. and Cahyono, N. (no date) ANALISIS SENTIMEN MENGENAI VAKSIN SINOVAC MENGGUNAKAN ALGORITMA SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM) DAN K-NEAREST NEIGHBOR (KNN).
[5] Citra Perusahaan, P., Melinda Savila, D. and Savitri Setyo Utami, L. (no date) Dela Melinda Savila, Lusia Savitri Setyo Utami: Strategi Corporate Social Responsibility dalam Strategi Corporate Social Responsibility dalam Pembentukan Citra Perusahaan (Studi pada Kegiatan CSR di PT. Wijaya Karya).
[6] Caytiles. R. D., dan Lee. S. (2014). A Review of an MVC Framework based Software Development. International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications, 8(10): 213-220.
[7] Fachrudin, M.F., Angkoso, C.V. and Fatah, D.A. (2024) ‘Analisis Sentimen Pada Sosial Media Twitter Terhadap Kualitas Jaringan Internet Telkomsel Menggunakan Ensemble K-Nearest Neighbour -Support Vector Machine’, Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Ilmu Komputer, 11(6), pp. 1253–1264. Available at: https://doi.org/10.25126/jtiik.2024118713.
[8] Fauziah, Y., Yuwono, B. and Aribowo, A.S. (2021) ‘Lexicon Based Sentiment Analysis in Indonesia Languages : A Systematic Literature Review’, RSF Conference Series: Engineering and Technology, 1(1), pp. 363–367. Available at: https://doi.org/10.31098/cset.v1i1.397.
[9] Fiarni, C. and Cellose, christell (2024) ‘Sentiment Analysis Of Indonesian Video Streaming Application Services Reviews Using Fine-Tuning Indobert And Aspect Modeling’, Journal of Computer Sciences and Informatics, (0), p. 1. Available at: https://doi.org/10.5455/JCSI.20240915104407.
[10] Hidayat, M., Prasetya, D. and Widiyaningtyas, T. (2025) ‘Sentiment Analysis of Latinized Arabic and Emoji in Indonesian YouTube Comments: A LABERT-LSTM Model’, Journal of Applied Engineering and Technological Science (JAETS), 6, pp. 1324–1341. Available at: https://doi.org/10.37385/jaets.v6i2.7000.
[11 ] Jamil, M., Hadiyanto, H. and Sanjaya, R. (2024) ‘Sentiment Analysis: Classifying Public Comments on YouTube in Disaster Management Simulation in Indonesia Using Naïve Bayes and Support Vector Machine’, Ingenierie des Systemes d’Information, 29(2), pp. 437–446. Available at: https://doi.org/10.18280/isi.290205.
[12] Norlaila, N., Winarno, W.W. and Luthfi, E.T. (2024) ‘Analisis Sentimen Masyarakat Tentang Tambang Di Indonesia Pada Twitter Menggunakan Data Mining’, JIPI (Jurnal Ilmiah Penelitian dan Pembelajaran Informatika), 9(3), pp. 1091–1099. Available at: https://doi.org/10.29100/jipi.v9i3.5402.
[13] Nurhaliza, D. and Andiyansari, P. (2024) Strategi Public Relations PC. GKBI dalam Membangun Citra Positif Perusahaan, Jurnal Indonesia : Manajemen Informatika dan Komunikasi (JIMIK). Available at: https://journal.stmiki.ac.id.
[14] Pratiwi, C.D., Damayanti, R.W. and Laksono, P.W. (2023) ‘Public Sentiment Analysis to Support Indonesian Government Induction Stove Program’, in E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202346502006.
[15] Putri, W.R.E. et al. (2025) ‘Exploring Public Sentiment on Green Economy Policy: A Natural Language Processing-Based Analysis’, International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 15(2), pp. 560–565. Available at: https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.18360.
[16] Saputra, M. and Sri Wahyuni (2024) ‘ANALISIS SENTIMEN PENGGUNA PADA APLIKASI BANK DIGITAL KROM DENGAN ALGORITMA SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE’, INFOTECH journal, 10(2), pp. 327–332. Available at: https://doi.org/10.31949/infotech.v10i2.11801.
[17] Suandi, F. et al. (2024) ‘Enhancing Sentiment Analysis Performance Using SMOTE and Majority Voting in Machine Learning Algorithms’, in, pp. 126–138. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6463-620-8_10.
[18] Stoneman, R. (2008). Alexander the Great: A life in legend. Yale University Press.
[19] Tineges, R., Triayudi, A. and Sholihati, I.D. (2020) ‘Analisis Sentimen Terhadap Layanan Indihome Berdasarkan Twitter Dengan Metode Klasifikasi Support Vector Machine (SVM)’, JURNAL MEDIA INFORMATIKA BUDIDARMA, 4(3), p. 650. Available at: https://doi.org/10.30865/mib.v4i3.2181.
[20] Tri Nugroho, B. and Noorlistyo Adi, A. (2024) ‘Sinergi International Journal of Communication Sciences Sentiment Analysis to Know Public Perception Regarding to Public Communication of Indonesian Customs and Excise’, 1(2).
[21] Wahyudi, R. et al. (2021) ‘Analisis Sentimen pada review Aplikasi Grab di Google Play Store Menggunakan Support Vector Machine’, JURNAL INFORMATIKA, 8(2). Available at: http://ejournal.bsi.ac.id/ejurnal/index.php/ji.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Intan Kusumadewi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
An author who publishes in the J-ENSITEC (Journal of Engineering and Sustainable Technology) agrees to the following terms:
- Author retains the copyright and grants the journal the right of first publication of the work simultaneously licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal
- The author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book) with the acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- The author is permitted and encouraged to post his/her work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of the published work






